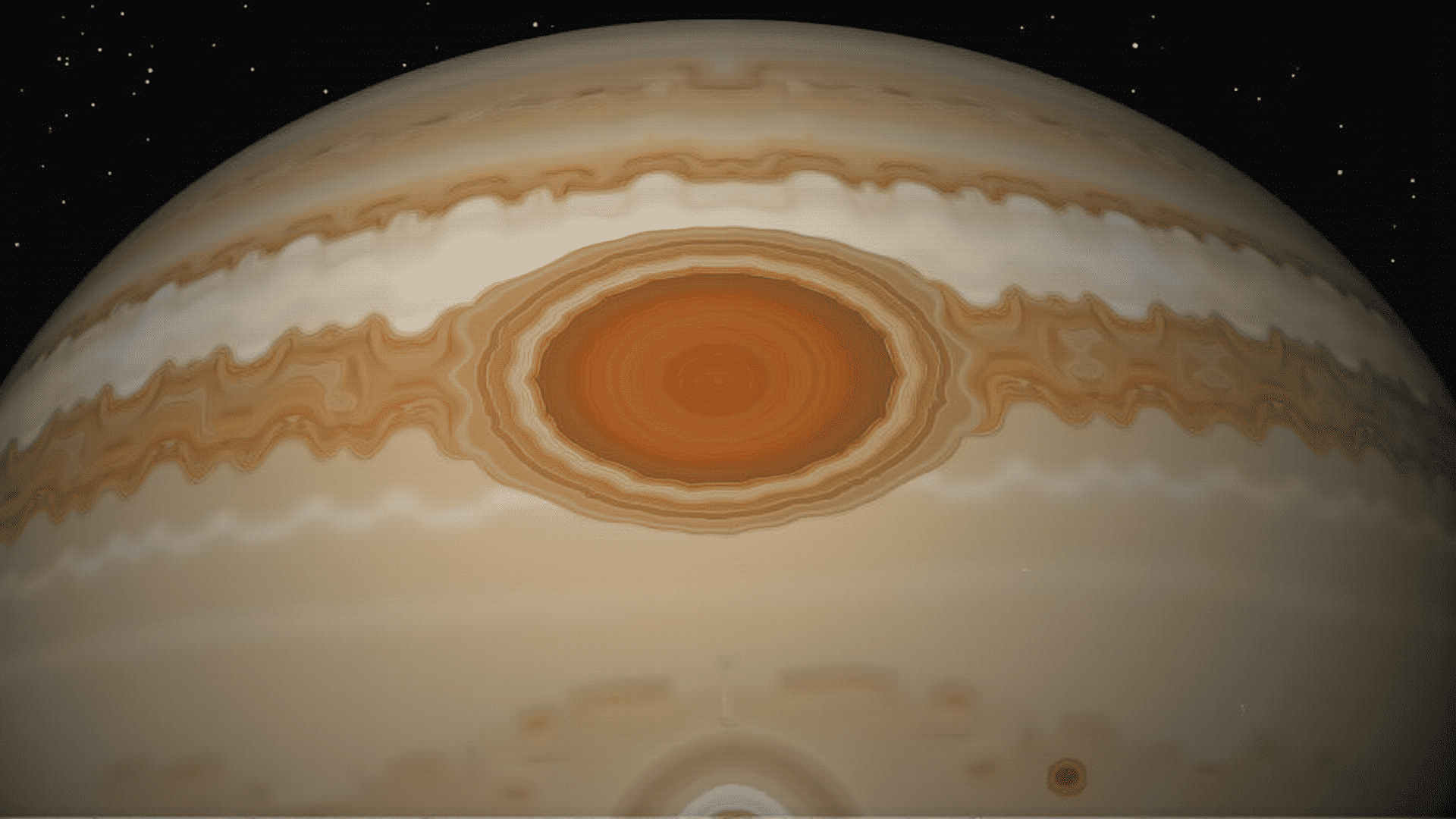
The Great Red Spot is one of the solar system's most captivating phenomena, stirring curiosity and wonder for centuries. Located on Jupiter, this massive storm is roughly 1.3 times the diameter of Earth, making it the largest known storm in our planetary neighborhood. However, its grandeur is not only in its size but also in its persistent presence. This article will dive into the mysteries of this iconic tempest, exploring its size, composition, and the science behind its enduring activity.
The first recorded sighting of the Great Red Spot dates back to the 17th century, suggesting it has been active for at least 350 years. Over time, astronomers have observed changes in its size, shape, and color, offering vital clues to understanding its dynamics. It's known that Jupiter's atmosphere primarily consists of hydrogen and helium, yet the conspicuous brick-red hue of the storm hints at more complex interactions. Some scientists speculate that the color may result from compounds like ammonium hydrosulfide reacting with ultraviolet light from the sun, though the exact process remains a subject of research.
An intriguing aspect of the Great Red Spot is its longevity. Unlike storms on Earth, which dissipate due to the friction against the planet's surface and interactions with varying air masses, Jupiter's lack of a solid surface allows its weather systems to exist undisturbed in the planet's thick gaseous atmosphere. Furthermore, the storm is fueled by Jupiter’s internal heat and the planet's rapid rotation, which creates the necessary conditions for its persistence. The Great Red Spot is essentially a high-pressure region, with counter-clockwise winds reaching speeds of up to 432 kilometers per hour.
Despite its long history, recent observations suggest that the Great Red Spot is gradually shrinking. Data gathered by telescopes and spacecraft reveal it is currently smaller than at any point in recorded history. While it is unclear whether it will eventually dissipate entirely, this shrinkage offers scientists a unique opportunity to study the factors influencing its size and lifespan.
In addition to its size and color, another remarkable feature of the Great Red Spot is its role as a natural laboratory for studying atmospheric physics. The storm's dynamics provide insights into fluid mechanics and storm formation, offering parallels to terrestrial weather patterns and enhancing our understanding of planetary atmospheres as a whole.
In conclusion, Jupiter's Great Red Spot remains one of the most fascinating subjects of astronomical study. Its grandeur, enigmatic nature, and potential to reveal new scientific insights ensure that it will captivate human imagination for many years to come. As technology advances, we can hope to uncover more about this stormy enigma, further expanding our knowledge of the universe.